Companies are set up in different ways depending on the objective of the business and the vision of the founder(s).
In this guide, you will understand the various types of companies that exist in Nigeria as well as the pros and cons of setting up any one of these.
Different Types of Companies in Nigeria
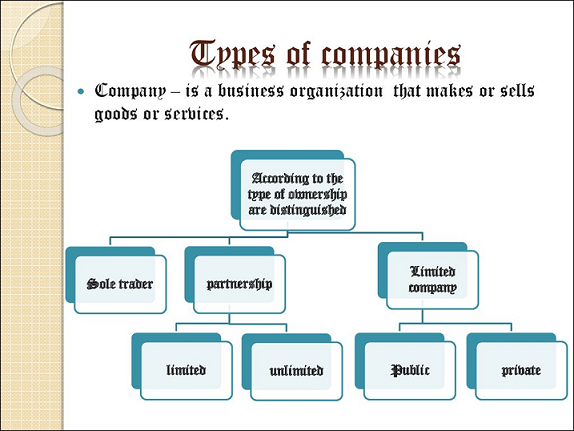
Sole proprietorship
This is the simplest form of enterprise. Thousands of businesses operate with this model with the founder as the sole owner of the business.
To start this kind of business, you just need to register your business name with the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC). However, there are many sole traders in Nigeria that are unregistered.
This type of business has the advantage of the founder enjoying all of the profit but this also means that the owner bears all of the risk of the company.
Based on the business setup, the sole trader is responsible for all aspects of the business and has unlimited liability to all debts and legal actions.
Due to the way the business is set up, a sole trader may find it difficult to attract outside investment or partners, which can hinder the expansion of the business.
Additionally, the sole trader may also find it difficult to attract business or contracts as s/he doesn’t file accounts or records with the CAC which may mean that the business lacks transparency. Also, this type of business makes it impossible for potential customers to verify the background of the business via an official third party.
Private Limited Company (Ltd)
A private limited company is a legal entity in its own right and in this case, the company is differentiated from the owner or its shareholders.
As a shareholder of a private limited company, the shareholders’ personal possessions remain separate (unless they are secured against the business for borrowing), and the shareholders’ risk is reduced to only the money they have invested in the company and any shares the shareholder holds which has not be paid for.
It is the most commonly registered business in Nigeria and it is often considered as prestigious by other companies and the general public due to its legitimate nature and the way important information is recorded at the Corporate Affairs Commission.
If you’re dealing with a limited liability company, you can easily verify the legitimacy of the company by checking the shareholders of the company and the financial status of the company. However, you will be asked to pay a small fee by the Corporate Affairs Commission.
The shareholders of the private limited company and its shares cannot be offered to the general public, unlike those of a public limited company.
As a result, the liability of the shareholders to creditors of the company is limited to the capital originally invested, i.e. the nominal value of the shares and any premium paid in return for the issue of the shares by the company.
Consequently, the shareholder’s personal assets are protected in the event of the company’s insolvency, but any money invested in the company may be lost.
Additionally, the disclosure requirements of the private limited company are lighter and as stated earlier its shares may not be offered to the general public and therefore cannot be traded on a public stock exchange.
Most small and medium scale businesses are privately held. In Nigeria, the private companies usually have the suffix “Limited” (often written “Ltd” or “Ltd.”)
In some cases, it can also be represented as “Incorporated” (“Inc.”) as part of the name.
There are several requirements when starting a limited liability company
- The company must have a registered office in Nigeria
- The company name must not be exactly identical to any other company name currently held in the registry of the Corporate Affairs Commission
- At least twenty five per cent of the authorised shares must be allotted at incorporation
- At least two people above the age of 18 must subscribe to the memorandum and articles of association.
- The total number of members in a private limited company must not exceed 50, not including those who are bona fide in the employment of the company
- The authorised share capital shall not be less than 10,000
Public Limited Company
This type of company differs from the private limited liability company because it is able to sell its shares to the public and may be quoted in the stock exchange.
However, a public company must have at least 500,000 authorised share capital and the subscribers must take up at least twenty-five per cent of the authorised share capital.
Generally, the cost of running a public limited company is reasonably higher than that of a private limited liability company and it is, therefore, better suited for large organisations.
Public Company Limited by Guarantee
A guarantee company is not for profit and it is the type mostly formed by charitable organisations. A guarantee company does not have share capital, and the members do not own the company as they do not receive any profits and have no claim to the company’s assets.
All income generated is used to cover operating costs and to achieve the objectives of the company
The share capital of guarantee or unlimited (ULtd.) company is similar to the limited company (Ltd., or PLC.) counterparts, but in this case, the liability of the members or shareholders is not limited
Private Unlimited Company
A private unlimited company is an incorporated company but it may be with or without a share capital. It is similar to the private limited company but in this case, the legal liability of the members or shareholders is not limited: that is, its members or shareholders have a joint, several and non-limited obligations to meet any insufficiency in the assets of the company to enable settlement of any outstanding financial liability in the event of the company’s formal liquidation.
Also, it is important to note that the joint, several and non-limited liability of the members or shareholders of such unlimited company to meet any insufficiency in the assets of the company (to settle its outstanding liabilities if any exist) applies only upon the formal liquidation of the company. Therefore, prior to any such formal liquidation of the company, any creditors or security holders of the company may have recourse only to the assets of the company, not those of its members or shareholders.
Until such an event occurs (formal liquidation), an unlimited company is similar with its counterpart, the limited company, in which its members or shareholders have no direct liability to the creditors or security holders of the company during its normal course of business or existence.
There are certain situations where setting up an unlimited company is preferred to its limited company counterpart. These scenarios are highlighted below:
- There is the need for secrecy concerning financial affairs hence the unlimited company effectively shields and protects the company’s financial affairs from public, media and competitor analysis, making them non-public information, including shareholder dividend payments: an unlimited company, unlike its limited company counterpart, is by the very nature of its legal liability generally not required to publish or make public its company financial statements
- The company is active or trading in an area where limited liability is not acceptable, vital or practical, but perpetual succession is important.
- The unlimited company extends a greater assurance and confidence to creditors and trade financial transactions, in contrast to its limited company counterpart.
- This type of company confers a low risk of insolvency.
- The company or its trading activities has or generates sufficient capital, funds or financing without need to approach general lenders such as high-street retail banks.
- The unlimited company provides a more advantageous company and business capital strategies in an ever-increasing irreversible trend of bank disintermediation by companies and their management.
- There is the need for a focused higher standard of board of directors and executive management behaviour (or probity) and business model for risk management.
Once an unlimited company is formed or incorporated, it doesn’t negate the fact that it can still be re-registered and converted into a limited company status. However, a few formalities will need to be carried out.
Also, a limited company can also re-register and designate itself to unlimited company status.
Wrapping up
If you’re looking to register any of these business types, you can visit the CAC Office close to you or you can visit the commission’s website.
The Federal Government has made the process of registering a business quite easy by enabling citizens do so from the comfort of their homes.
Now you can register your business online. The incorporation of the business can be done and processed online. This includes the availability search and the registration process. All you need do is visit the website of the CAC.
Also, you don’t always have to use a third party to register your company except in certain cases. For instance, in the case of the incorporation of a company, the process cannot be concluded unless an accredited agent has duly certified such application for registration.