Economists around the world use income per capita as an important metric to gauge the domestic productivity of a country as it shows how much economic value can be attributed to each citizen. In this article, we’ll be discussing what income per capita is all about, including providing information on how to calculate the average income earned per person in a given geographical area. All that will be discussed concerning per capita income and its calculation applies to Nigeria as with any other country of the world. Read on.
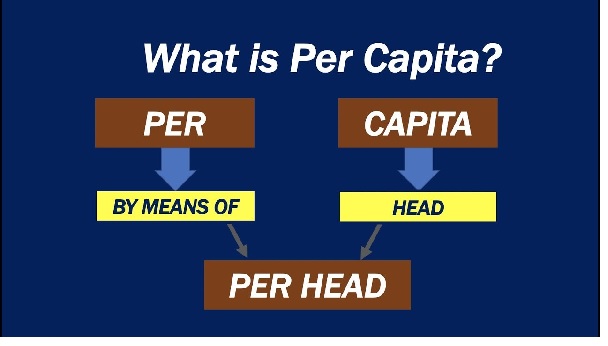
How to calculate income per capita in Nigeria would be discussed below:
-
What Does Income Per Capita Mean and How is it Calculated?
Income per capita is a common term used in economics, business, and statistics disciplines to assess the level of living and the quality of life of individuals in a certain geographical entity, for example, Nigeria. It is a major measure of calculating the Human Development Index (HDI) of a nation by determining a country’s per-head income.
The income per capita is derived by dividing the combined nation’s income by its total population. To understand better how income per capita is computed, we must discuss what the gross domestic product of a country is because that’s how a nation’s combined income is derived.
-
What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
The gross domestic product (GDP) of a country refers to the total monetary market value of the finished goods and services produced within its borders within a specified period. To derive the combined income of a country in a specified period, GDP encompasses all private and public consumption, government outlays, investments, paid-in construction costs, and total exports.
GDP computation can be on a nominal basis or a real basis. Nominal GDP calculation involves the assessment of the total monetary value of all the goods and services within a country using current prices. Simply put, the nominal computation of GDP doesn’t factor in rising prices, which can inflate the growth figure.
Real GDP, on the other hand, accounts for inflation in the price of goods and services produced by an economy in a given year. Since inflation tends to increase the value of the gross domestic product of a country’s economy, real GDP considers the differences in prices between the current year and the base year. With the GDP adjusted for inflation, it becomes easy to tell if real expansion in production or inflation was responsible for the increase in a country’s economy.
-
How to Determine the Gross Domestic Product of a Country’s Economy?
There are three methods to determine the total monetary market value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country in a specified year. These methods of calculating GDP include the expenditure approach, production approach, and income approach. Each of these methods could be computed on a nominal basis or a real basis, but the latter expresses long-term national economic performance better.
The expenditure approach to calculating the gross domestic product of a country’s economy involves taking into account the different groups that spend in the economy. This approach is calculated using the formula below:
GDP = C + G + I + NX
where C = consumer spending or private consumption expenditures
G = government spending and gross investment
I = private domestic investment or capital expenditures
NX = net export
The production method of determining GDP, also known as the output approach, measures the input costs that contribute to economic activity and deducts the cost of goods and services consumed in the production process.
The income approach method of calculating GDP considers the income earned by the entire factors of production in the economy. Wages and salaries paid to employees, rents earned by land, corporate profits, and returns on capital in the form of interest, are some examples of income earned by factors of production in an economy. Indirect business taxes and depreciation are also taken into account when the income approach is used in calculating GDP.
-
Illustration on How Income Per Capita
As stated earlier, income per capita is derived by dividing the total gross domestic product, adjusted by the inflation of a country by its total population. Since this article is about how to calculate income per capita in Nigeria, let’s illustrate how income per capita is calculated using the available data on the GDP and population of the country.
According to official data from the World Bank, Nigeria’s GDP was USD 477.39 billion in 2022. The population of Nigeria for 2022, according to the WorldMeter website is 218,541,212.
Using the above data let’s calculate the income per capita of Nigeria for 2022:
Income per capita = $477,390,000,000/218,541,212
= $2184.44
Therefore, $2184.44 is the income per capita for Nigeria for 2022.
-
Limitations of Income Per Capita as a Human Development Index
There exist some limitations of income per capita that are worth mentioning. One of those challenges is that income per capita fails to account for the income disparity of the citizens of a country. Another limitation of income per capita, particularly when it’s not adjusted for inflation, is that inflation tends to increase the GDP and ends up exaggerating a population’s income.
Another limitation of income per capita is that it includes children as part of the overall population, even when they do not make any money. As a result, the value of income per capita of a nation’s economy is distorted. In addition, income per capita does not take into consideration the quality of hours and working conditions of the labour force, their educational level, and medical benefits, which in turn, doesn’t paint a clear picture of the average living standard and productivity of the population.
Furthermore, individual savings and wealth of the population of a country are not considered when calculating income per capita. This means that a rich person, for instance, could have a modest annual income from not working but rely on savings to live an affluent life. In such a situation, the rich individual would thus be represented as a modest earner if the income per capita statistic is used.